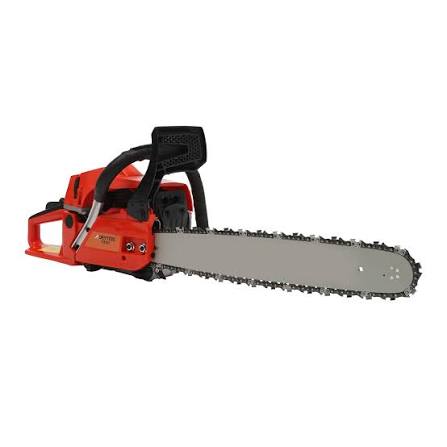
A chainsaw is a portable power saw that cuts through wood using a set of sharp teeth attached to a rotating chain. In 2026, modern models have evolved to include high-efficiency stratified-charge gas engines or advanced 36V/40V brushless electric motors, emphasizing reduced emissions and quieter operation.
Core Components and Mechanics
The standard chainsaw consists of three primary systems: the power unit, the drive mechanism, and the cutting system.
Power Source:
Gasoline Engines: Typically two-stroke engines (30cc to 120cc) that offer the highest power-to-weight ratio for heavy-duty forestry.
Electric Motors: Available in corded (unlimited runtime near power) or cordless battery (portable, low maintenance) versions.
Drive Mechanism: Uses a centrifugal clutch that allows the engine to idle without moving the chain. As engine speed increases, the clutch engages a drive sprocket, which pulls the chain around the bar.
Cutting System:
Guide Bar: An elongated steel plate (typically 30cm to 90cm) with a groove that supports and directs the chain.
Saw Chain: An "endless chain" of links including cutters (with sharp teeth and depth gauges), drive links, and tie straps.
Safety Features (2026 Standards)
Modern chainsaws are engineered with multiple "failsafe" systems to protect the operator from kickback and accidental contact.
Chain Brake: Stops the chain within milliseconds if a kickback occurs or if the front handguard is pushed forward.
Chain Catcher: A metal or plastic hook that seizes a derailed or broken chain, preventing it from swinging toward the user.
Throttle Lockout: A safety trigger that must be depressed before the throttle can be activated, preventing accidental starts from brush or sticks.
Anti-Vibration System: Uses springs or rubber bushings to decouple the engine from the handles, reducing operator fatigue and long-term joint damage.
Inertia Brake: Automatically engages the chain brake during a rapid rotational force (kickback) even if the operator's hand does not touch the guard.
Common Applications
Forestry & Logging: Felling trees, limbing branches, and processing logs into firewood.
Construction & Specialized Use: Modified chainsaws with diamond-grit chains are used for cutting concrete, stone, and brick.
Artistic Carving: Specialized "dime-tipped" or narrow bars allow for precision in chainsaw sculptures.
Disaster Relief: Quick clearing of fallen trees and debris following storms.
Would you like a side-by-side comparison of the top-rated gas and battery chainsaws for 2026 to help determine which power source fits your typical usage?